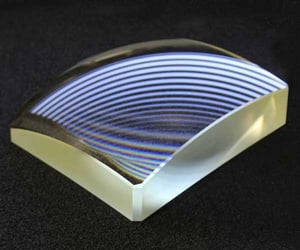
Cylindrical Optics
Manufacturing cylindrical lenses presents numerous challenges, particularly as mechanical geometries influence process selection and capabilities. Manufacturers must possess a deep understanding of how various techniques impact cylinder specifications, enabling them to offer design recommendations that optimize cost-efficiency and improve tolerances.
At Optimax, our customers benefit from a dedicated team of experienced engineers who leverage advanced manufacturing processes to deliver tailored solutions, rather than just products.
What are Cylinder Lenses?
Cylindrical optics are a type of lens with a curvature in a single direction, yielding different radii in the X and Y axes. Optical cylinders are subsequently ideal for condensing, focusing, or expanding incoming light. Optimax fabricates cylinders from a range of materials, utilizing a deterministic CNC machining process to ensure predictable removal rates and tight adherence to critical tolerances.
The surface curvature of cylindrical optics is typically spherical and they tend to have a plano-convex or plano-concave design, coming in circular, rectangular, or square profiles. These are used for a broad range of applications across the full spectrum of industry and research. Common uses of cylindrical lenses include correcting astigmatism and altering the shape of laser beams prior to collimation.
OEMs rely on optical cylinders for various purposes in holography, optical spectroscopy, laser line scanning, and more. Those same OEMs depend upon Optimax to overcome critical manufacturing challenges and to routinely deliver the highest quality cylindrical optics.
Specifying Aspheric Optics
Specifying an asphere begins with a custom aspheric form, often fit to the Forbes Q Polynomial (Figure 1) or the Even Aspheric Equation (Figure 2).
Describing the form involves specifying Vertex Radius (I/C). Conic Constant (k) and applicable Aspheric Coefficients (a). Including a Sag Table (Figure 3) provides reference information to check correct data entry for each manufacturing or metrology tool used. We accept asphere designs from our customers in manufacturing drawing format or by optical design software files (preferably, Zemax).
Our team is well versed in providing manufacturability feedback and providing cost and lead time trade-offs for various tolerancing schemes. If you have a question about your design, don’t hesitate to contact Optimax.
Manufacturing Cylindrical Optics
Cylindrical lenses comprise an optical surface that has a radius in one direction and is flat in the orthogonal direction. The manufacturing methods used in cylinder manufacture account for this axis, subsequently conserving position. There are two primary production techniques used to fabricate cylindrical optics – the Arbor process and the X-Y process.
The radius of curvature divided by diameter – or width – gives an R-number, which helps define which technique should be selected. Alternatively, order quantity may be the determining factor in method selection. At Optimax, we pride ourselves on delivering a collaborative service, offering customers the benefit of our extensive expertise and assisting with the burden of choice.
FIND THE OPTIC SPECIFICATIONS RIGHT FOR YOUR NEEDS:
Manufacturing the Future
At Optimax, we are manufacturing the future, creating the highest precision optics underlying high-tech systems in key markets and applications. We offer rapid and expedited delivery upon request and are committed to our customers in the long term.
Submit an RFQ to begin your partnership with one of the world’s leading custom optics manufacturers, committed to long-term customer success.